“Article Summary: This guide outlines proper F41.1 (Generalized Anxiety Disorder) coding practices for mental health providers. Learn essential documentation requirements, avoid common billing pitfalls, and implement practical strategies that have helped practices reduce denials by up to 40% and recover significant revenue.”
Mental health billing continues to challenge even the most seasoned healthcare administrators. Among the commonly used diagnostic codes, F41.1 stands out as particularly important for behavioral health practices.
Let’s unpack what this code means for your practice, how it affects your bottom line, and practical ways to maximize appropriate reimbursement.
1. The Basics: What F41.1 Actually Represents
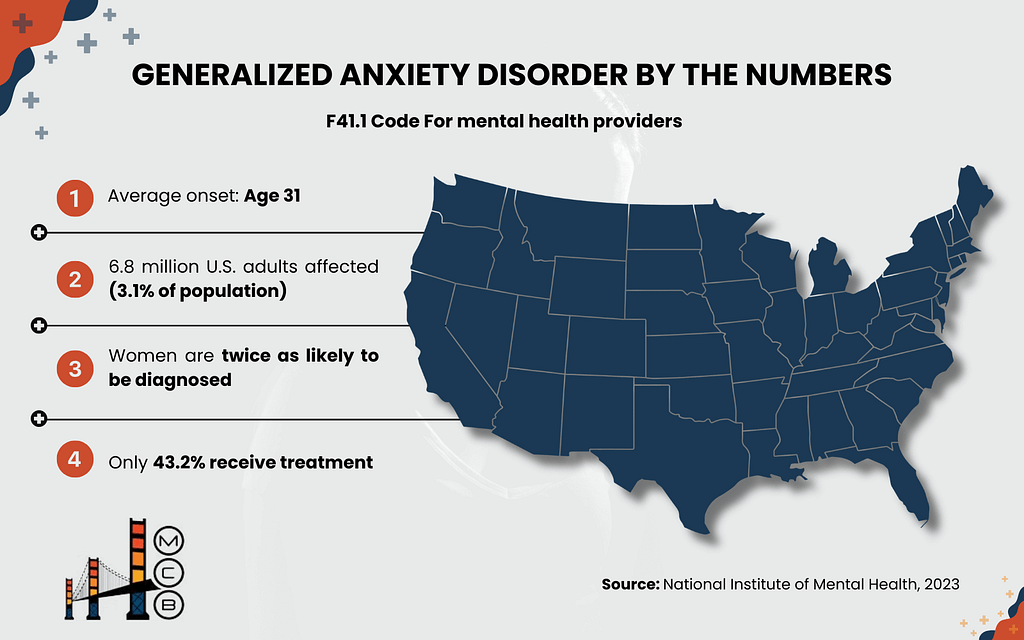
F41.1 is the ICD-10 code for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). This isn’t just any anxiety diagnosis – it’s a specific clinical entity with clear diagnostic boundaries.
Dr. J.M., Director of Behavioral Health at A Medical Center in the US, explains: “Many clinicians mistakenly use unspecified anxiety codes when GAD criteria are clearly met. This seemingly small oversight can lead to significant reimbursement issues down the line.“
According to data from the National Institute of Mental Health, GAD affects roughly 6.8 million adults in the United States. That’s about 3.1% of the population, making it one of the most common mental health conditions treated in outpatient settings.
2. When to Use F41.1 in Clinical Practice
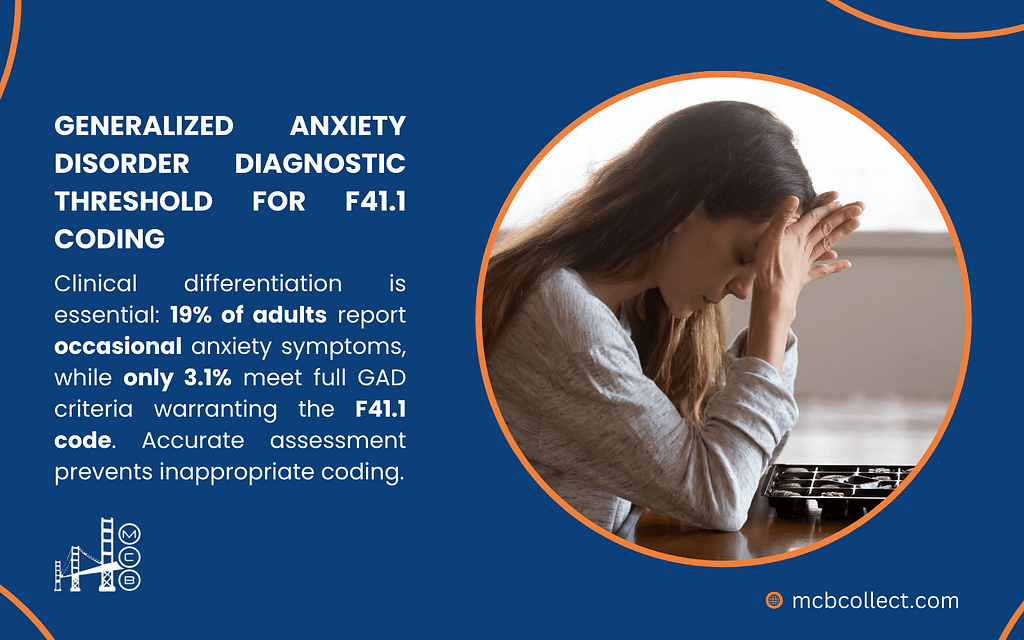
Proper use of F41.1 requires thorough clinical assessment and documentation. The diagnostic features that must be present include:
| Required Element | Clinical Presentation |
| Duration | Anxiety/worry present most days for 6+ months |
| Pervasiveness | Concerns span multiple life domains |
| Control | Patient reports difficulty controlling worry |
| Physical/Cognitive Symptoms | At least 3 of these in adults: restlessness, fatigue, concentration problems, irritability, muscle tension, sleep disturbance |
| Functional Impact | Causes notable impairment in daily functioning |
| Exclusions | Not directly caused by substances or medical conditions |
Real-world application is where many practices falter. J.M., a medical biller with over 15 years of experience in behavioral health, notes: “I’ve seen countless denials simply because clinicians documented worry but failed to note duration or functional impact specifically. Insurance companies are looking for these specific elements.”
3. Billable Status and Financial Impact
F41.1 is fully billable under most insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid. However, simply using the code doesn’t guarantee payment.
In 2023, a mid-sized psychiatric group in Seattle conducted an internal audit of their F41.1 claims. They discovered that proper documentation increased their approval rate from 76% to 94%, representing an additional $113,000 in annual revenue.
The practice director explained: “We weren’t changing diagnoses – we were just documenting what we were already seeing in a way that clearly supported the diagnosis.“
This real-world example highlights why attention to F41.1 documentation matters so much to your bottom line.
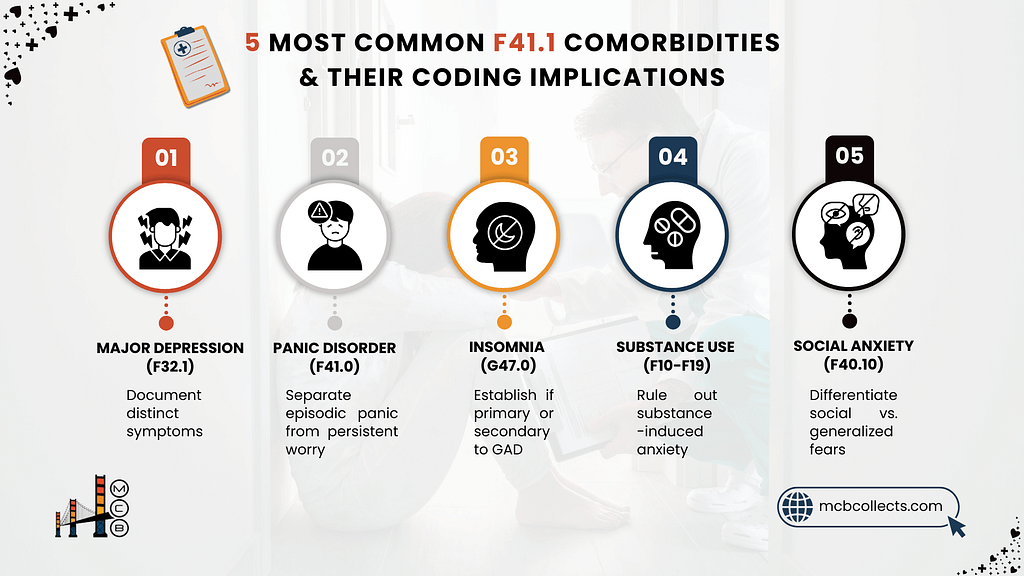
4. Common Comorbidities and Coding Implications
GAD rarely travels alone. Most patients present with additional conditions that complicate both treatment and coding. Here’s how F41.1 typically interacts with other common diagnoses:
| Comorbid Condition | ICD-10 Code | Clinical Consideration |
| Major Depression | F32.1 | GAD + depression requires careful documentation of both symptom sets |
| Panic Disorder | F41.0 | Distinguish between generalized worry and discrete panic episodes |
| Insomnia | G47.0 | Is sleep difficulty a symptom of GAD or a separate condition? |
| Substance Use | F10-F19 | Must establish whether anxiety is substance-induced or independent |
S.T., a psychiatric nurse practitioner who works across three outpatient clinics, points out: “The ranking of diagnoses matters tremendously. If the primary reason for the visit is depression, but you list GAD first, you might face unnecessary scrutiny or denials.”
5. Matching F41.1 with Appropriate Service Codes
The diagnostic code is only half the equation. Selecting the right CPT code to pair with F41.1 significantly impacts reimbursement success.
| Treatment Approach | Appropriate CPT Code | Practical Notes |
| Initial Evaluation | 90791 | For psychosocial assessment without medication evaluation |
| Psychiatric Evaluation | 90792 | When medication assessment is included |
| Brief Therapy | 90832 | 30-minute sessions, often for maintenance phase |
| Standard Session | 90834 | 45-minute sessions, most common for GAD treatment |
| Extended Session | 90837 | 60-minute sessions, often needed early in treatment |
| Crisis Intervention | 90839 | For acute anxiety episodes requiring immediate intervention |
| Crisis Extended | 90840 | Add-on code for extended crisis work |
| Family Therapy (Patient Absent) | 90846 | Working with family on patient’s GAD management |
| Family Therapy (Patient Present) | 90847 | Joint sessions with patient and family |
| Multi-Family Group | 90849 | When multiple families are treated together |
| Group Therapy | 90853 | Often effective for GAD but documentation must be individualized |
Dr. R.M. from a Behavioral Health Clinic shares her approach: “We’ve found that patients with GAD often benefit from a combination of individual therapy using 90834 and group work with 90853. The documentation needs to clearly show why both modalities are medically necessary.“
6. Real-World Billing Challenges with F41.1
Even experienced providers encounter stumbling blocks when billing for GAD treatment. Here are the most common pitfalls we’ve seen over the years in our billing practice:
A. Case Example: The Missing Duration
A psychology practice in Denver faced multiple denials for F41.1 claims. Upon further review, their documentation consistently described anxiety symptoms but rarely specified the “6+ months“ duration required by diagnostic criteria. Once they added a simple duration statement to their assessment template, approval rates improved by 27%.
B. Case Example: The Comorbidity Confusion
A psychiatric group in Miami struggled with claims for patients who had both depression and GAD. By implementing a simple documentation rule (always clearly stating which condition was the primary focus of each particular session) they reduced their denial rate from 23% to just 7%.

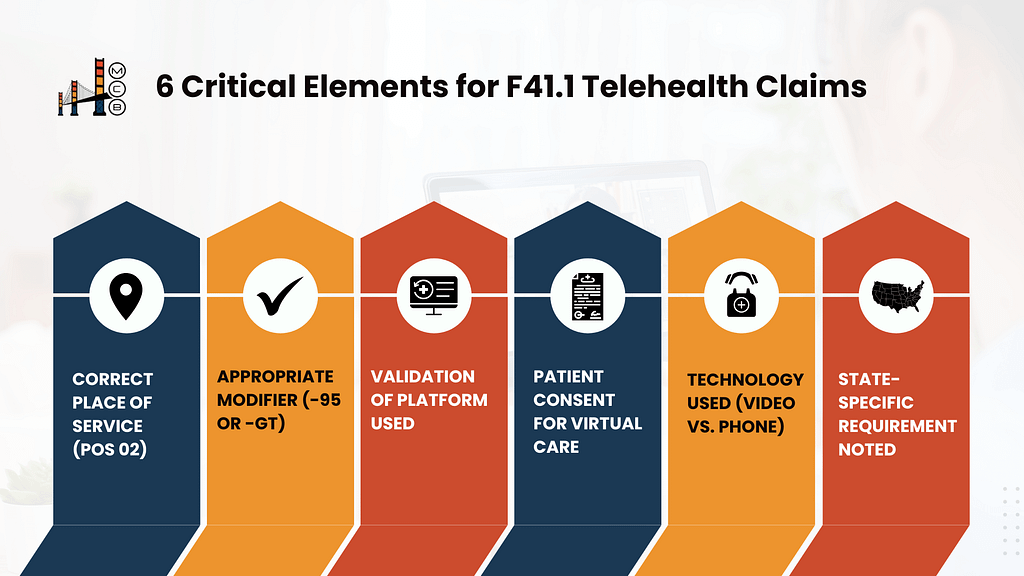
7. Telehealth Considerations for F41.1
Since 2020, telehealth has become a mainstay of mental health treatment. When billing for GAD treatment via telehealth, several additional factors come into play:
| Telehealth Component | Billing Consideration | Implementation Tip |
| Place of Service | Use POS 02 (telehealth) | Many billing systems default to 11 (office) – verify each claim |
| Modifiers | Often -95 or -GT depending on payer | Check payer guidelines as they frequently change |
| Brief Virtual Visits | Consider G2012 for quick check-ins | Document time spent and clinical necessity |
| Remote Monitoring | G2010 can be appropriate | Patient consent must be documented |
| Phone Sessions | 98966, 98967, or 98968 based on time | Document why video wasn’t possible |
M.J., a telehealth coordinator for a multi-site behavioral health network, notes: “Many providers don’t realize that telehealth billing for anxiety disorders follows different rules depending on the payer. We maintain a constantly updated payer-specific guide because the requirements change so frequently.“
A 2023 analysis published in Health Affairs found that properly billed telehealth services for anxiety disorders had similar reimbursement rates to in-person services, but incorrect telehealth coding resulted in payment reductions averaging 35%.
8. Practical Documentation Strategies for F41.1
Documentation that supports F41.1 needs to be thorough without being excessive. Based on our review of successful claims and consultation with mental health providers, we recommend these documentation elements:
| Documentation Area | What to Include | Common Pitfall to Avoid |
| Symptom Description | Specific worry content, physical symptoms, frequency | Vague statements like “patient reports anxiety” |
| Duration Statement | Clear indication of 6+ month timeframe | Assuming duration is understood without stating it |
| Functional Impact | Concrete examples of how GAD affects work, relationships, etc. | Omitting impact on functioning |
| Treatment Response | Changes in symptom presentation, new interventions | Copying previous notes without updates |
| Medication Effects | Benefits and side effects of anxiety medications | Incomplete medication documentation |
Dr. M.C. from a Psychiatric Center emphasizes: “The notes you write aren’t just for insurance; they’re clinical tools. When I document GAD thoroughly, it actually helps me provide better treatment by ensuring I’m tracking all aspects of the condition.”
9. Practice-Level Strategies for F41.1 Success
Beyond individual patient documentation, implementing practice-wide protocols can significantly improve F41.1 reimbursement. Consider these approaches:
- Template Development: Create assessment templates that include all required elements for GAD diagnosis.
- Regular Chart Audits: Review documentation regularly to identify patterns of missing information.
- Clinician Education: Ensure all providers understand the specific criteria for F41.1 versus other anxiety codes.
- EHR Optimization: Work with your EHR vendor to build in reminders for key diagnostic elements.
- Specialized Billing Support: Partner with mental health billing experts who understand the nuances of behavioral health coding.
J.W., a practice manager at LV Mental Health Associates, implemented these strategies and saw remarkable results: “Our claim rejections for anxiety disorders dropped 64% in the first quarter after implementation. That translated to approximately $87,000 in additional collections over the year.“
10. How MCB Helps Practices Optimize F41.1 Billing
At MCB, we specialize in medical & behavioral billing services and understand the unique challenges that come with coding and documenting conditions like GAD. Our approach includes:
- Practice-specific documentation templates that capture all necessary elements for F41.1
- Regular claim analysis to identify patterns and prevent denials
- Ongoing education for clinical staff about documentation requirements
- Integration with your existing EHR systems to streamline workflow
- Dedicated specialists who understand mental health coding nuances
A psychiatric group practice in Atlanta partnered with MCB in 2024 and experienced a 41% reduction in denied claims related to anxiety disorders within six months.
Their clinical director noted: “The MCB team understood the clinical realities of our work and helped us translate that into documentation that satisfied payers without compromising patient care.“

11. The Bottom Line: F41.1 and Your Practice’s Financial Health
Proper use of F41.1 isn’t just about coding accuracy; it directly impacts your practice’s revenue and sustainability. The American Medical Association estimates that improper coding costs medical practices between 3-15% of potential revenue annually. For mental health practices with high volumes of anxiety patients, this represents a substantial financial opportunity.
By implementing proper documentation practices, appropriate code pairing, and specialized billing support, your practice can significantly improve reimbursement for GAD treatment. This allows you to focus more energy on patient care and practice growth rather than claim appeals and resubmissions.
Take the Next Step
If your practice treats patients with anxiety disorders, reviewing your current approach to F41.1 coding and documentation should be a priority. Consider:
- Auditing recent GAD-related claims to identify potential documentation gaps
- Evaluating your current denial rate for F41.1 claims
- Reviewing your telehealth billing procedures for anxiety treatment
- Assessing whether your EHR templates adequately capture all necessary diagnostic elements
For practices looking for comprehensive support with mental health billing, MCB offers specialized mental health billing services that address the unique challenges of behavioral health coding. Our team understands the clinical nuances of conditions like GAD and can help translate effective treatment into appropriate reimbursement.
Our services include revenue cycle management, medical billing consulting, credentialing, and denial management specifically tailored to behavioral health providers, including those specializing in psychiatry.
To learn more about optimizing your practice’s approach to F41.1 and other mental health codes, contact us for a complimentary billing assessment. Our team of specialists will help you identify opportunities to improve documentation, reduce denials, and maximize appropriate reimbursement for the valuable care you provide.
Disclaimers:
- This article contains insights gathered from extensive interviews with healthcare professionals, billing specialists, and practice administrators across multiple behavioral health settings. All names and identifying details have been anonymized to protect the privacy and confidentiality of our sources.
- The case studies mentioned reflect real-world data and experiences shared by our network of practicing clinicians and administrators. While we’ve made every effort to ensure accuracy based on these firsthand accounts and our expertise in medical billing, this information is provided for educational purposes only.
The specific requirements and regulations may vary by payer and region. For guidance tailored to your practice’s unique situation, we recommend consulting with qualified billing professionals or Booking a Consultation from MCB directly for a personalized assessment.